Phi designer course consultation 13681274966 is the same as wechat Guogong
. 
The thermal comfort of human body depends on the indoor environment, that is, indoor temperature, relative humidity and air flow velocity
. 
The optimal range of thermal comfort is 18 ~ 25 ℃ in winter and 30% ~ 80% in relative humidity; 23 ~ 28 ℃ in summer and 30% ~ 60% in relative humidity; the indoor air flow velocity is 0.1 ~ 0.7m/s
. 
Temperature and humidity monitoring system of human body’s heat balance, the main ways of human body’s outward heat dissipation are: conduction, radiation, convection, evaporation
. 
The human body is constant temperature
. 
If the heat released by the human body is greater than the heat generated by its metabolism, the human body will feel cold
. 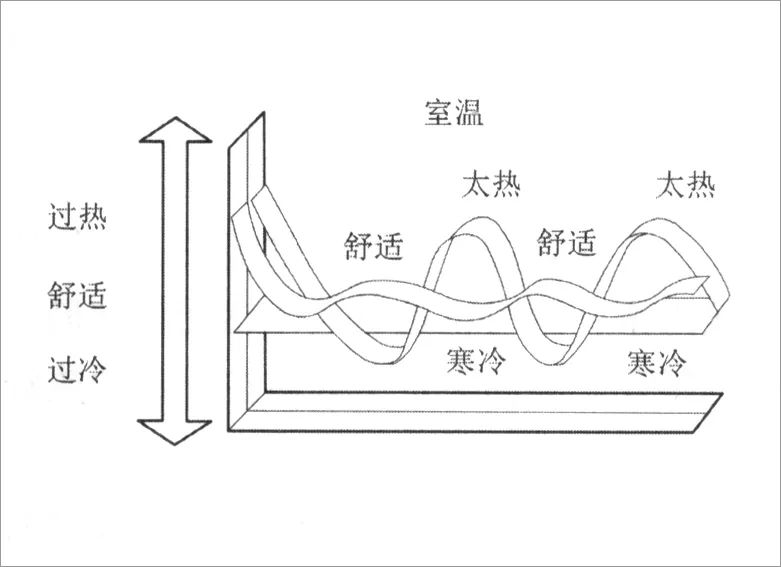
On the contrary, if the heat released by the human body to the environment is less than the heat generated by its metabolism, the heat will accumulate in the human body, and the human body will feel hot
. 
Appropriate building comfort can provide a good working and living place to avoid the occurrence and infection of various diseases, which is of great benefit to the rest and maintenance of human body and plays an important role in the improvement of human health
. 
The subjective factors influencing human thermal comfort are metabolic rate; people with high metabolic rate are not afraid of cold, but afraid of heat; people with low metabolic rate are not afraid of heat, but afraid of heat Cold clothing situation: different types of buildings, different functional rooms, people’s clothing situation is not the same
. 
Objective factors: air temperature: the most important factor, directly determines the feeling of the human body is cold or hot
. 
The most suitable indoor temperature for human body is 24 ~ 28 ℃, and the relative humidity of air: high relative humidity makes people feel stuffy and sticky; low relative humidity makes people uncomfortable to breathe, and a large amount of floating dust in the air further pollutes the indoor air
.
The relative humidity of indoor air in winter should be 40% ~ 80% and the air flow velocity will indirectly affect the thermal comfort of human body
.
Air flow can take away the waste gas emitted by the human body and reduce the concentration of carbon dioxide around the human body
.
Appropriate speed can increase the evaporation of the human body surface, giving people a fresh feeling
.
The best air velocity in winter is 0.2 ~ 0.5 m / s
.
Objective of thermal comfort basic objective: comfort ideal standard: healthy development trend: high efficiency and energy saving thermal comfort problems in heating period in China excessive or insufficient heating: different from solar radiation, the room in the south is overheated, which causes people to open windows to cool down and lose heat, outdoor dust also pollutes the indoor air; the room in the north is low temperature and uncomfortable
.
Poor air mobility, serious pollution: old buildings do not pay much attention to building ventilation, indoor oxygen content will be low, high concentration of dioxide, great harm to human body
.
Winter indoor dry, low relative humidity: less precipitation in northern areas, high indoor temperature, large air evaporation, more pollutants, more water loss of human body, will feel dry discomfort
.
Improvement means active intervention: artificial and active intervention by building equipment passive improvement: thermal inertia of building envelope, better use of nature and building itself rather than relying on building equipment to intervene passive improvement means, to avoid short board effect, to strengthen thermal insulation capacity: for the thermal insulation performance of buildings, the thermal insulation of building envelope The capacity is determined by the part with the worst insulation performance
.
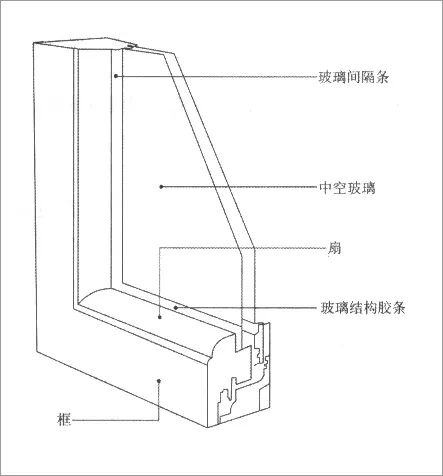
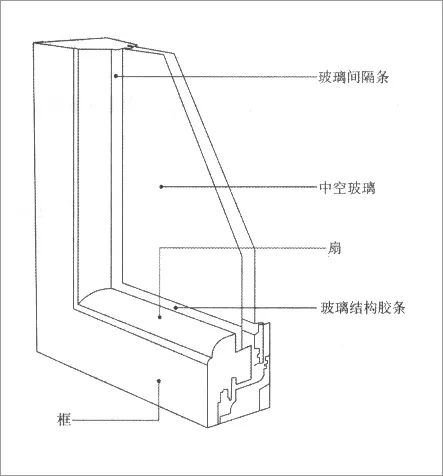
The glass in the window is the weakest part of the building thermal capacity, so it should be specially designed
.
In addition, it is necessary to avoid the cold bridge caused by unreasonable design
.
Low-E glass enhances heat gain ability through greenhouse effect: “greenhouse effect” is a typical way of solar energy heat gain, which should be reasonably applied in cold winter
.
There are mainly two kinds of passive solar energy design: direct heating and indirect heating
.
Direct heat gain is to store solar radiation heat into various heat storage bodies of buildings, and then release it gradually at different times; indirect heat gain is to receive and store solar energy by heating various heat media, and then heat indoor air or various indoor heat storage bodies by heating various heat media
.
Direct heating is the most effective and economical
.
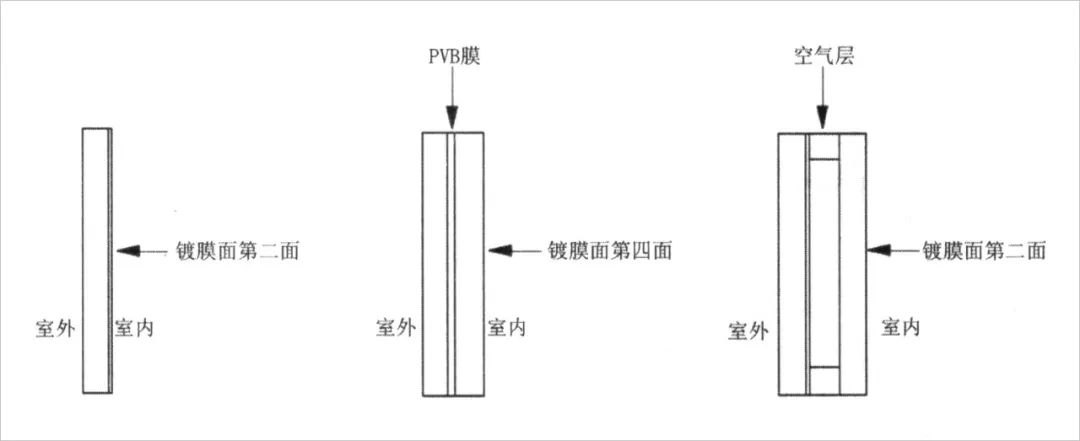
Comparison of different Low-E glass (left figure) single Low-E energy-saving glass (middle figure) glued Low-E energy-saving glass (right figure) single hollow Low-E energy-saving glass strengthens time lag effect through heat storage design: the control of indoor temperature largely depends on the configuration of heat insulation materials and heat storage materials, and reasonable setting will cause the phenomenon that the change of indoor temperature lags behind the change of outdoor temperature, This is the “time lag” phenomenon
.
Setting climate buffer zone to control thermal comfort: common climate buffer zones include cold proof door, closed balcony, north auxiliary room, etc
.
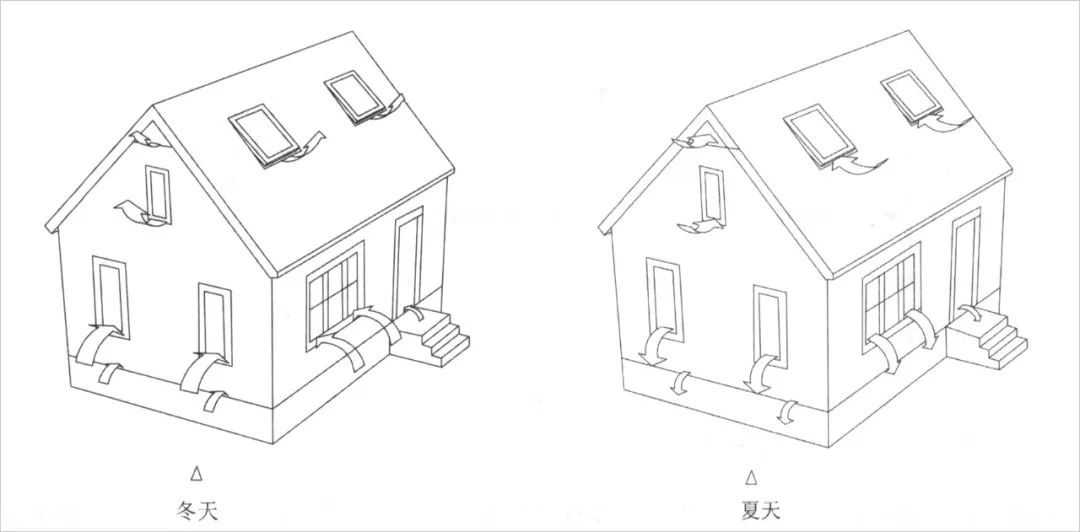
(left) schematic diagram of chimney effect in winter of independent residence (right) schematic diagram of chimney effect in summer of independent residence uses chimney effect to control indoor air convection and exchange air: due to different temperature and height, air pressure difference will be caused, thus forming the movement of indoor air flow, which is called “chimney effect”
.
In passive design, chimney effect not only improves the thermal comfort of buildings, but also plays an important role in designing a healthy and clean indoor space
.
Book / conference / Phi
.