In this way, we hope that students and the public will not become far away from the culture of the past
. 
The next year, his family moved to Liverpool
. 
The architectural design work won the Alva Alto award in 1976, the Royal Institute of architects Gold Award in 1980, the Pritzker Architecture Award in 1981 and the Thomas Jefferson Gold Award in 1986
.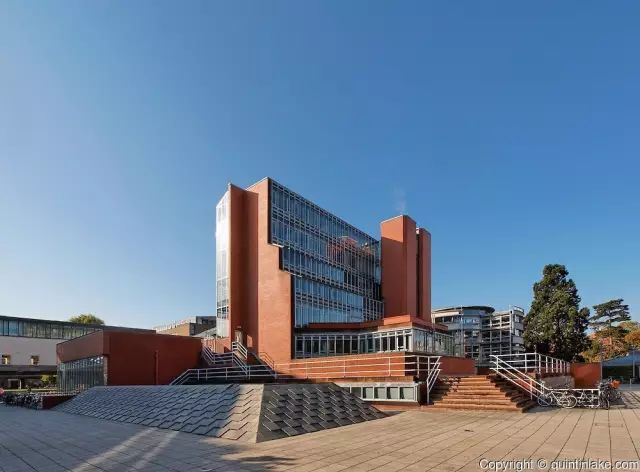 
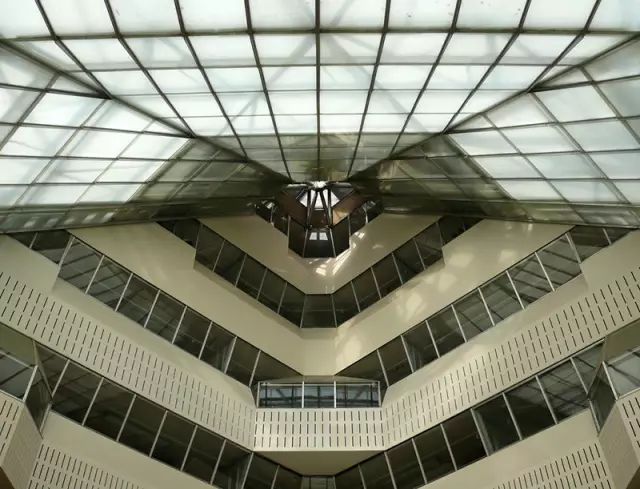
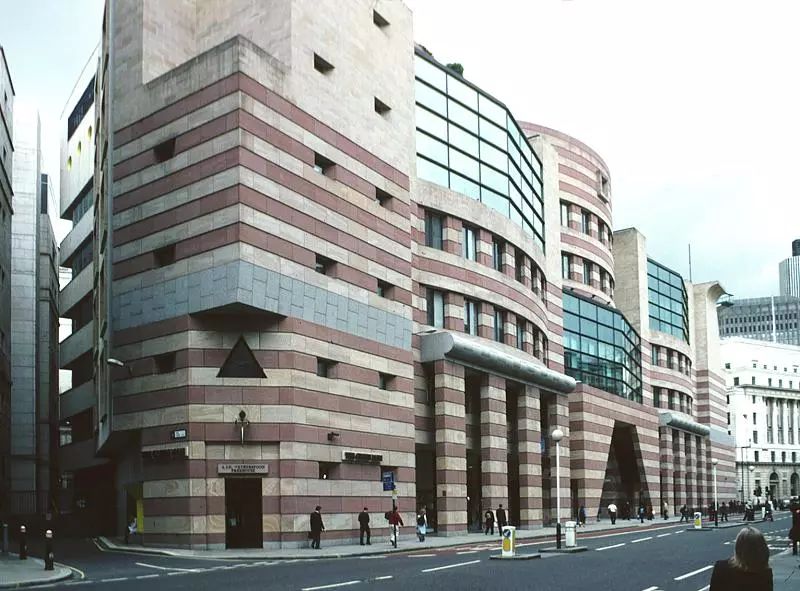
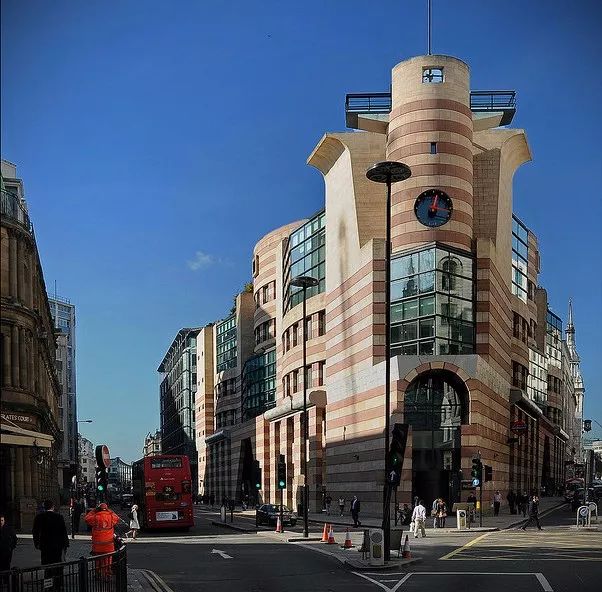
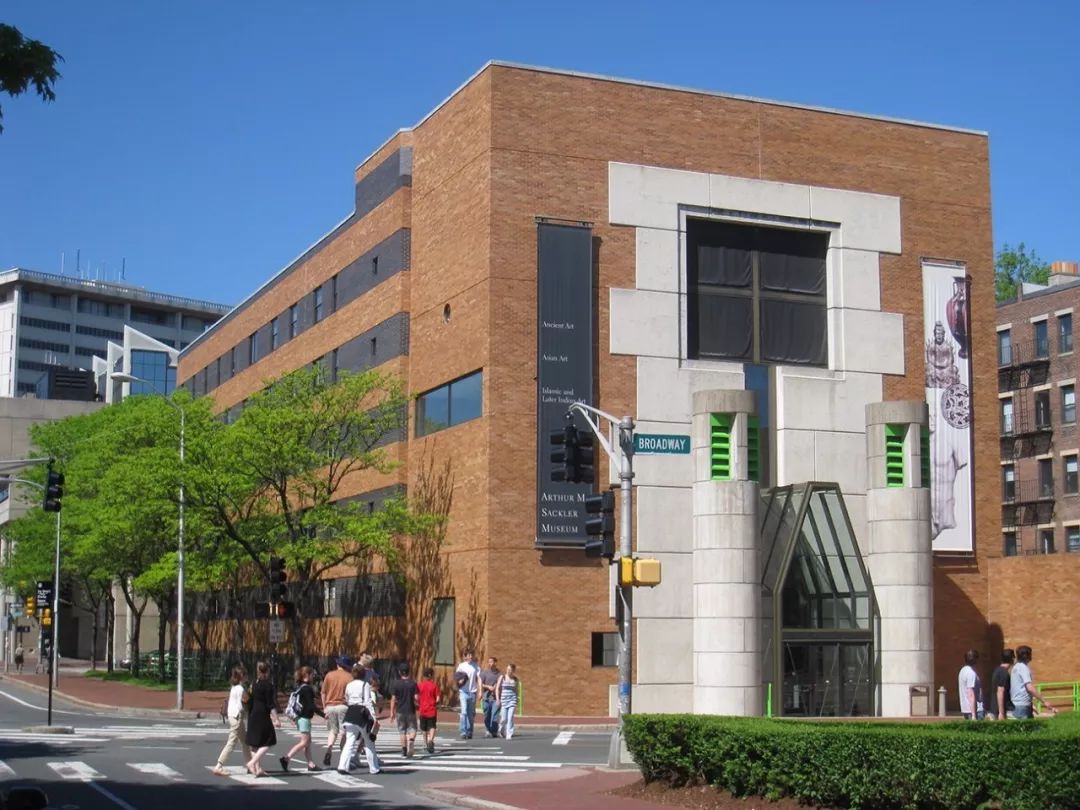
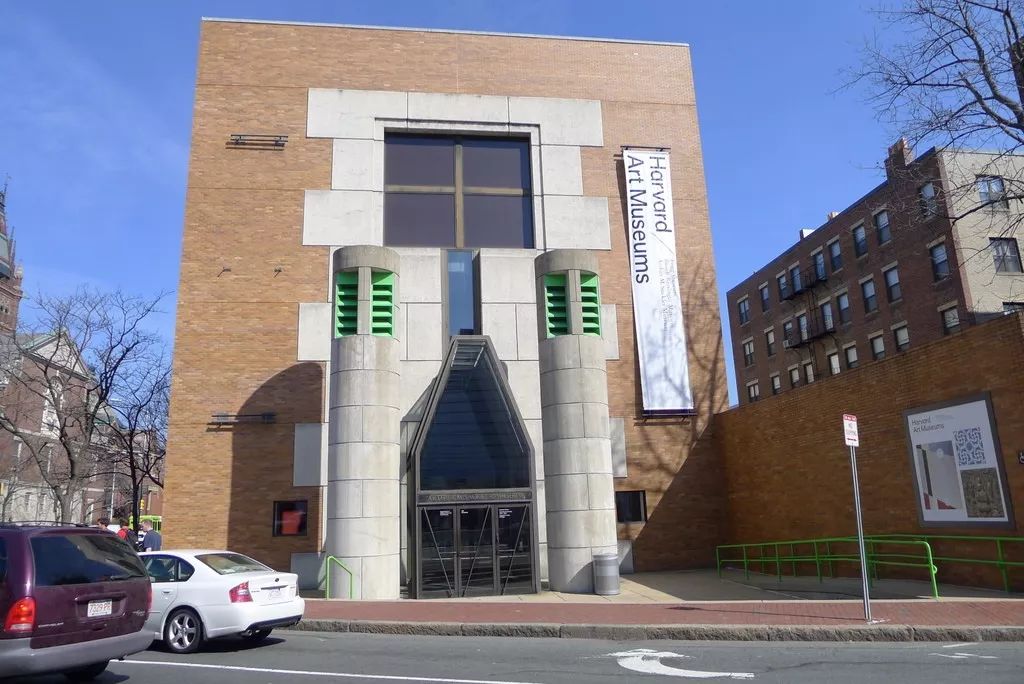
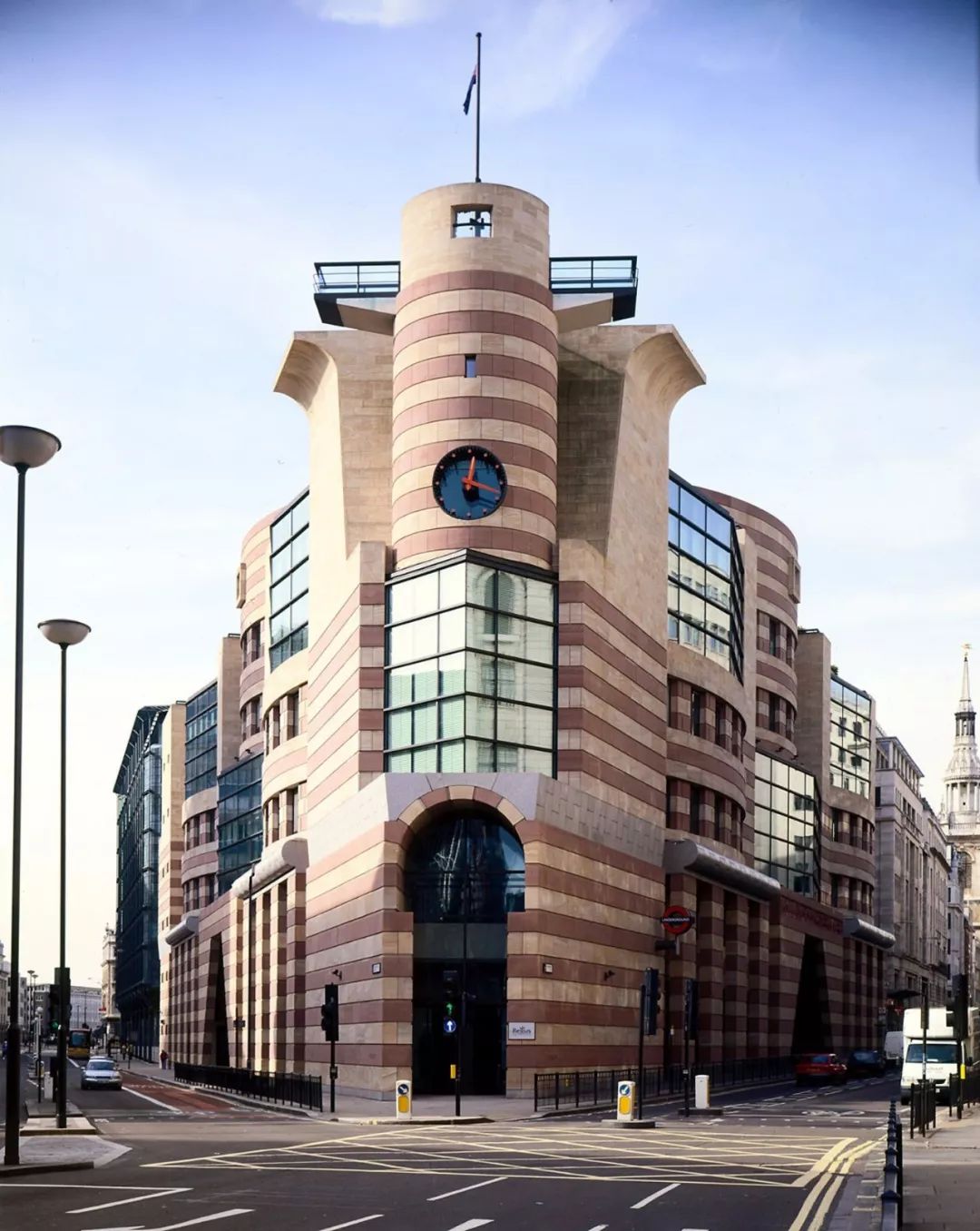
The most famous ones are the new building and experimental theater of Stuttgart National Museum of art designed from 1977 to 1984, the sacro Museum of Harvard University from 1979 to 1984, and the London Museum of art from 1980 to 1986
. 
At that time, it was located in a small area close to Victoria Park
. 
At the same time, as a senior partner, he cooperated with Lyons, Israel and Ellis to work from the school of architecture This started his career in architecture
. 
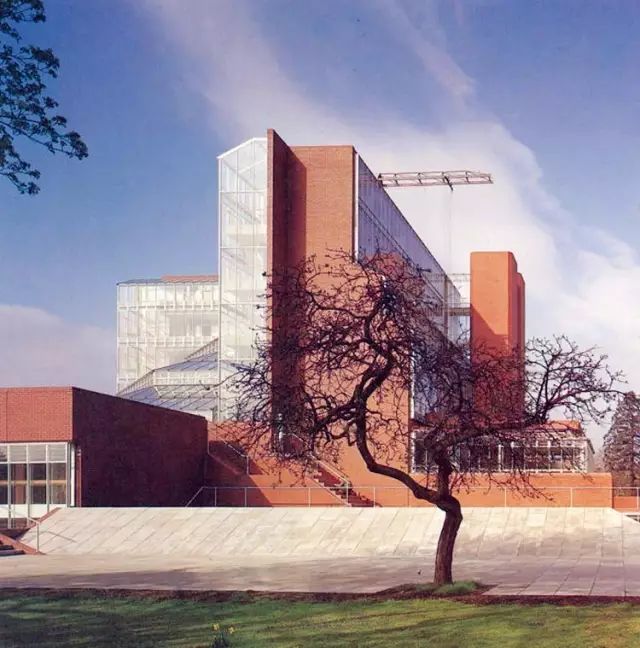
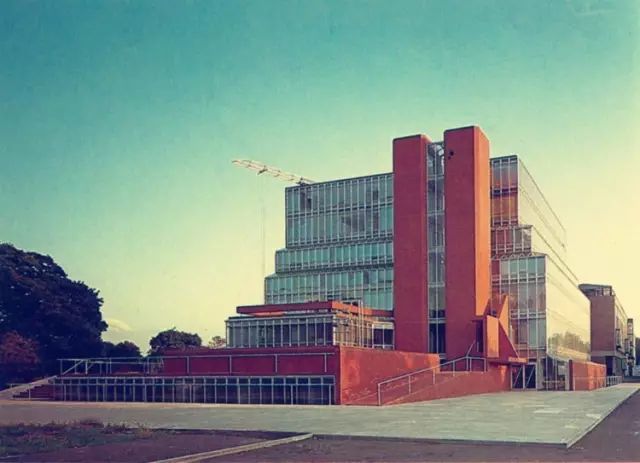
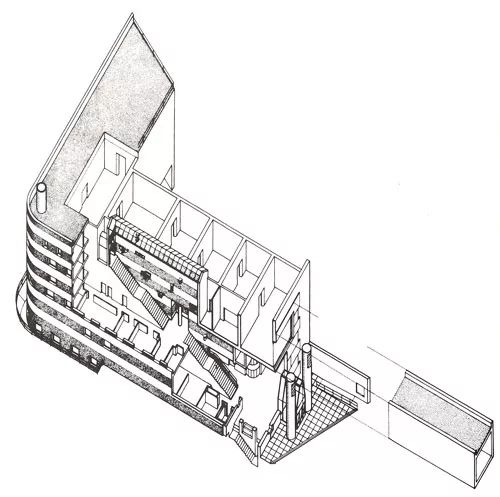
The building itself is composed of a high tower on one side and a large mechanical experiment workshop
.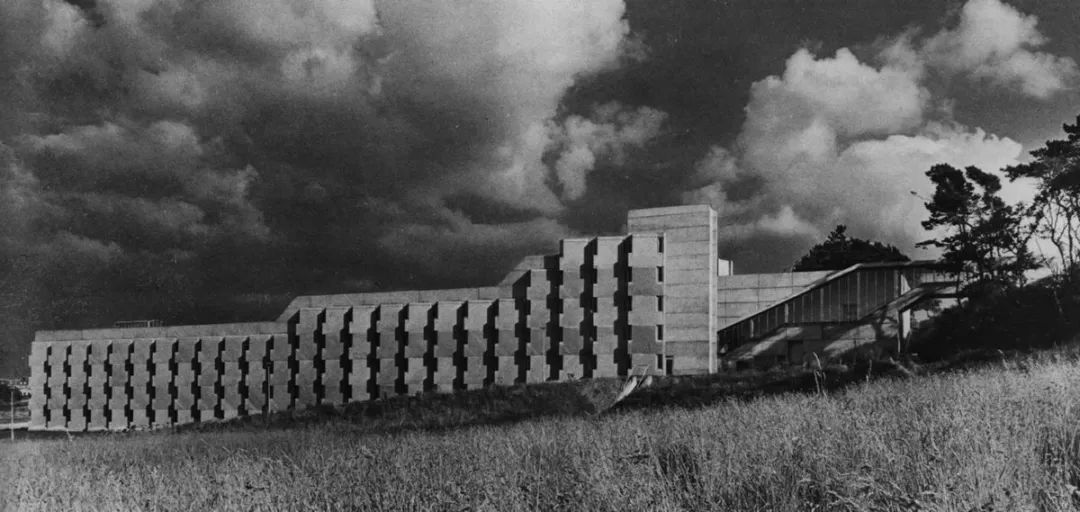 
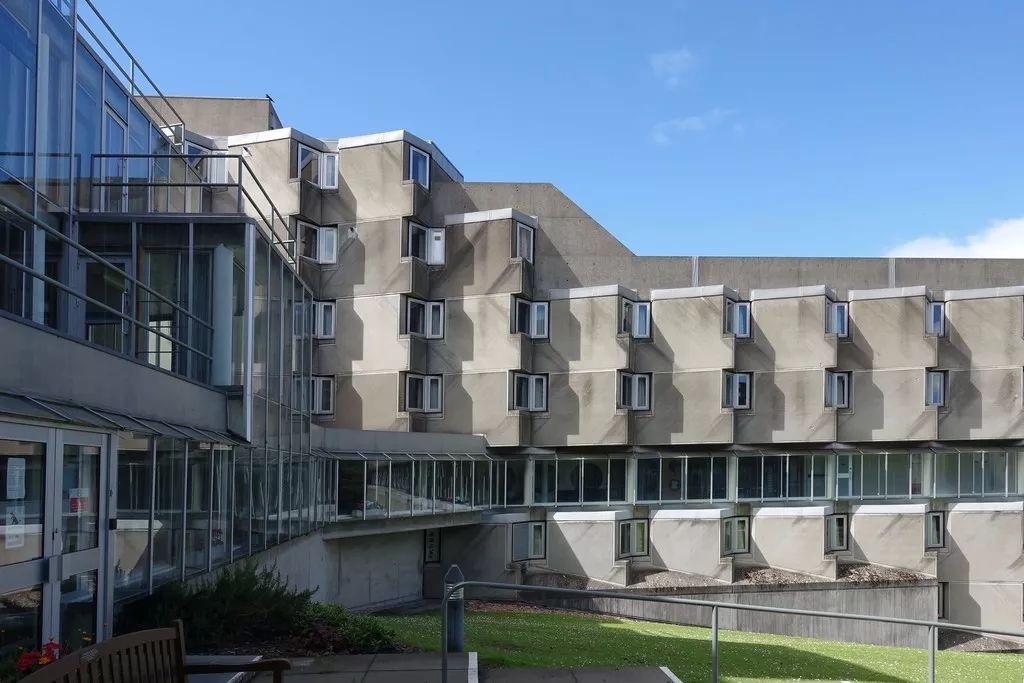
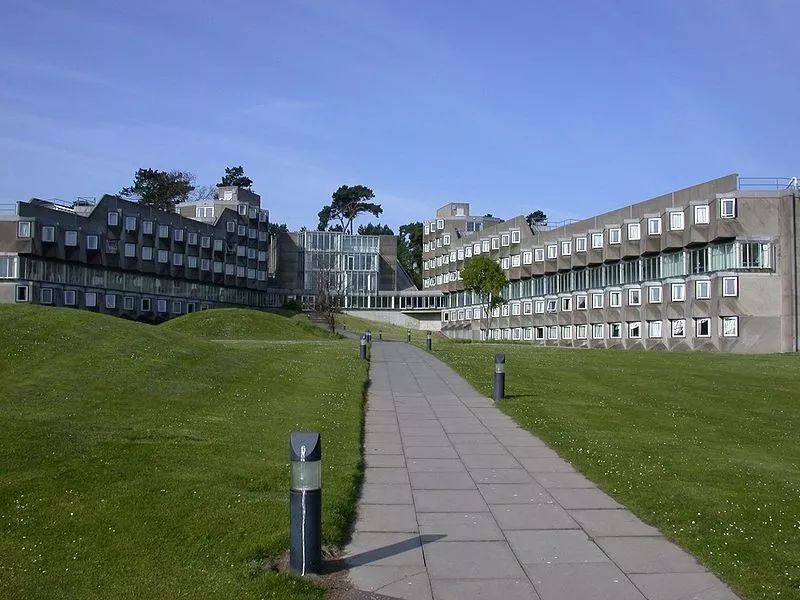
Representative works 1 the engineering building of Leicester University, built from 1959 to 1963, is a famous work of James sterling
. 
The ventilation chimney and building components are conducive to the formation of ventilation, making the museum the largest natural ventilation building in Europe
. 
Stirling once said: “I believe that the shape of a building should imply – or express – its purpose and user’s way of life, which is why its shape should be diverse, not similar
. 
In order to provide sufficient space for students, the British government approved the construction of high-rise buildings for universities for the first time
. 
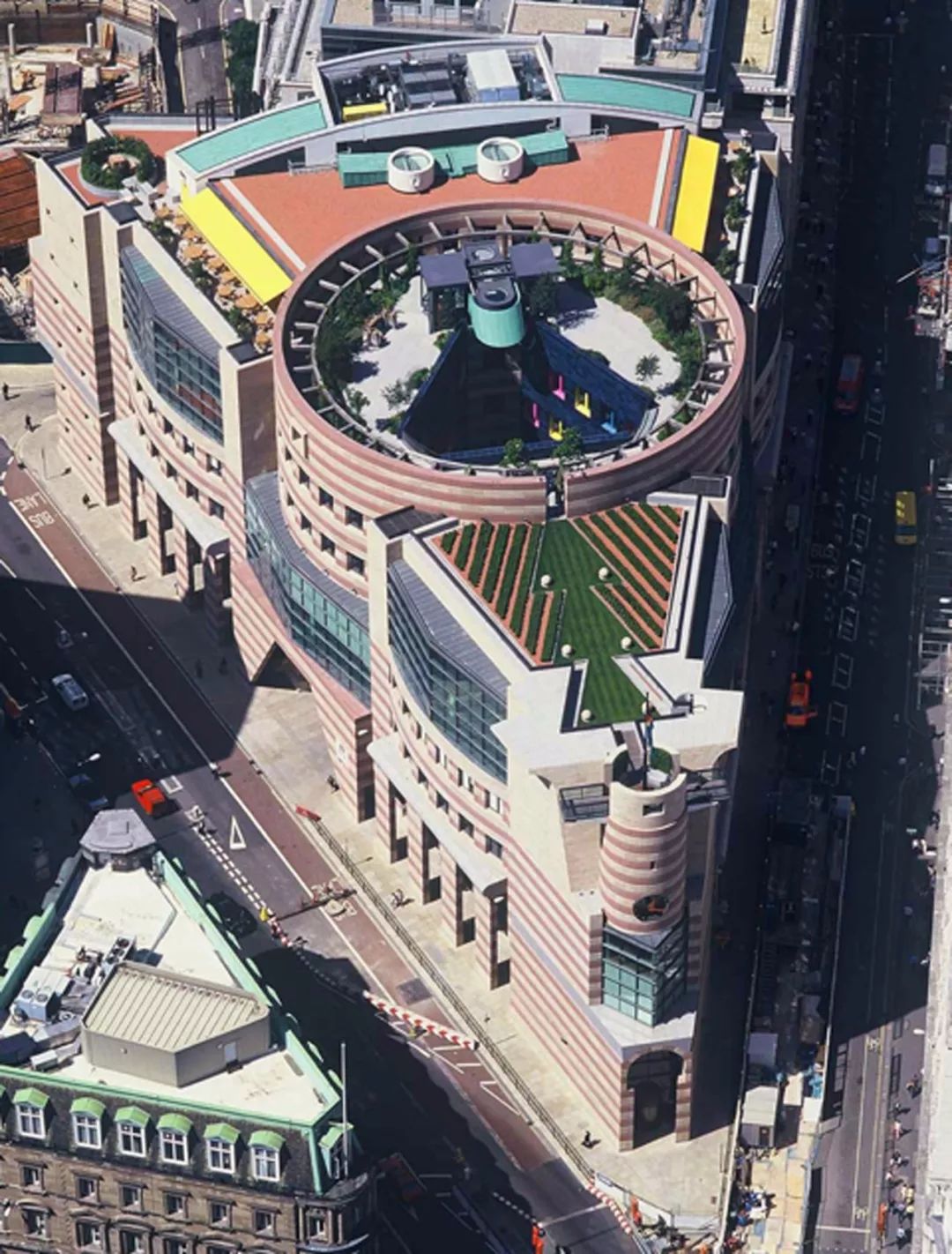
The selection and application of materials all reflect James Stirling’s attention to function
. 
The whole roof is derived in the form of 45 ° sharp angle upward
. 
James Stirling was born in Glasgow, Scotland in 1926
. 
He has also taught in Europe and has been a professor at Yale since 1967
. 
The overall design image is not only with the characteristics of the machine age, but also in harmony with the simple style of the campus
. 
James Stirling emphasizes that his works are not “indulging in stupid post-modern self indulgence”, “functionalism” is still the primary principle of his design and the basis of all design ideas
. 
When talking about design philosophy, he said: “I firmly believe that the logical analysis of the base site and the functional interpretation of the project will inevitably and naturally produce the scheme.” In the late 1960s, some architects and theorists put forward a new architectural trend of thought, which mainly reflected and criticized the theory and practice of modern architectural schools, and thus led to a fierce collision between cultural theory and concept schools in various fields
. 
James Stirling (1926-1992) is generally regarded as the pioneer of British contemporary architects and a creative postwar international architect
. 
The engineering Museum of Leicester University with large truss structure was the largest natural ventilation building in Europe at that time
. 
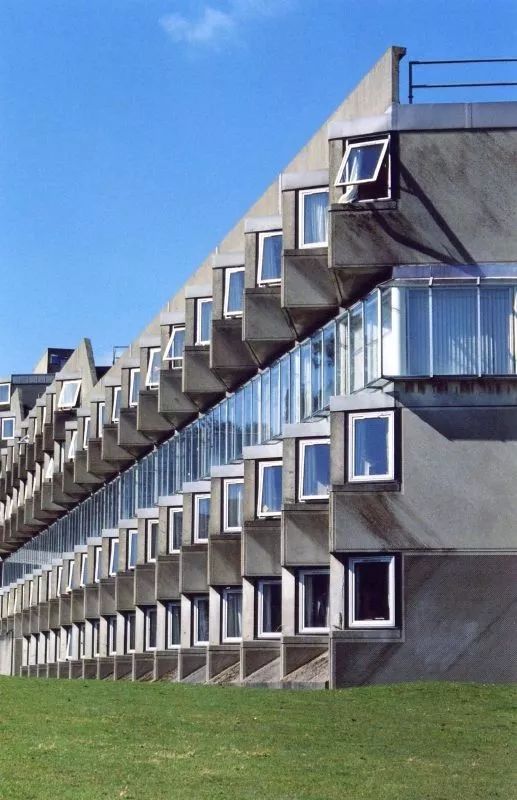
From 1950 to 1957, most of James Stirling’s architectural works were residential buildings, such as the low-cost residential buildings in North London designed in 1953 and the ham site residential buildings designed from 1955 to 1958
. 
In 1959, he designed the engineering Museum of Leicester University and became famous
. 
“Stairs and elevators are respectively set in two concrete shafts, in which toilets and up and down pipes are also set, so that the space in the two towers is very flexible and can be arranged and changed according to the needs.
. 
Most of his architectural works are museums with varied styles
. 
He thinks that “functionalism” theory is “the main contribution to the development of architecture in the 20th century”
. 
Although his early and later works are quite different, he always adheres to the design principle of “functionalism”
. 
Since then, his projects have expanded to museums, art galleries, libraries and theaters
. 
Therefore, the 1970s has become the watershed of James Stirling’s architectural creation: in the previous stage of creation, most of the architectural projects undertaken by James Stirling were houses with strong functionality and low cost; in the latter stage, most of them were cultural large-scale projects such as museums, reflecting the change of James Stirling’s design ideas of more respecting context and returning to essence
. 
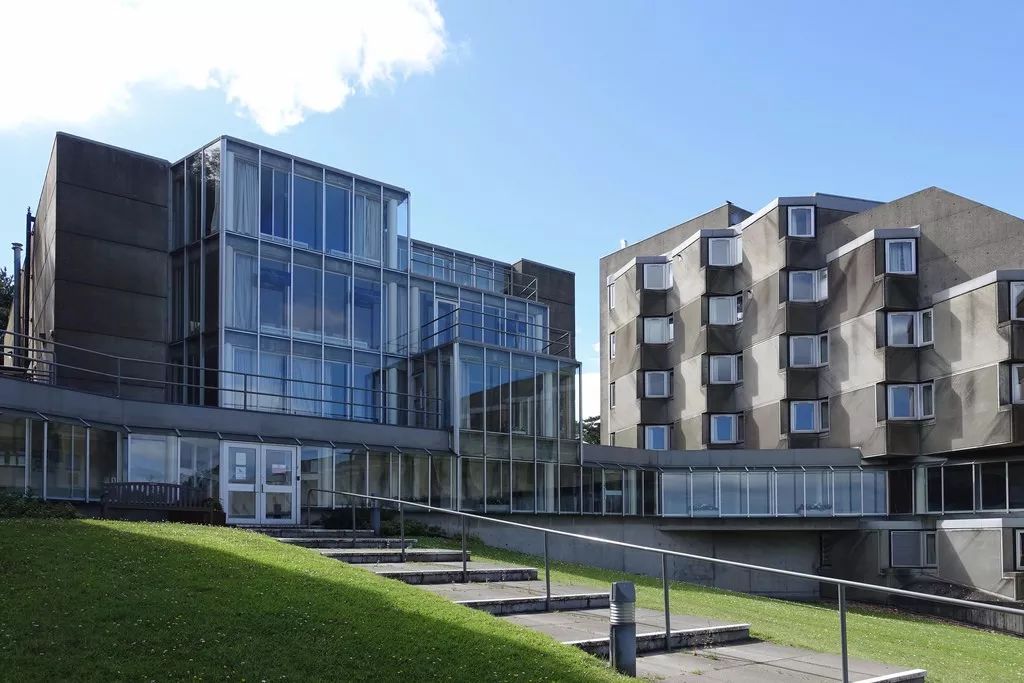
The two towers are connected by the middle glass traffic shaft
. 
Since 1971, Stirling has been working with Michael Wilford
. 
The division of structure and the use of materials of the engineering Museum of Leicester University are both rational and original
. 
James Stirling intended to separate the mechanical air handling system
. 
In his youth, James Stirling won the Awal awatar award in 1977, the RIBA gold medal in 1980 and the Pritzker Architecture Award in 1981
. 
People often label him as “postmodernism”, but for him, this is a misunderstanding
.
Among them, the most famous are ham common’s garden style apartment (1955-58), Leicester University’s seed engineering building (1959-63) and Cambridge University’s historic building (1964-67)
.
In order to ensure the workshop to meet the needs of sufficient lighting, James Stirling boldly adopts a large-span transparent glass roof
.
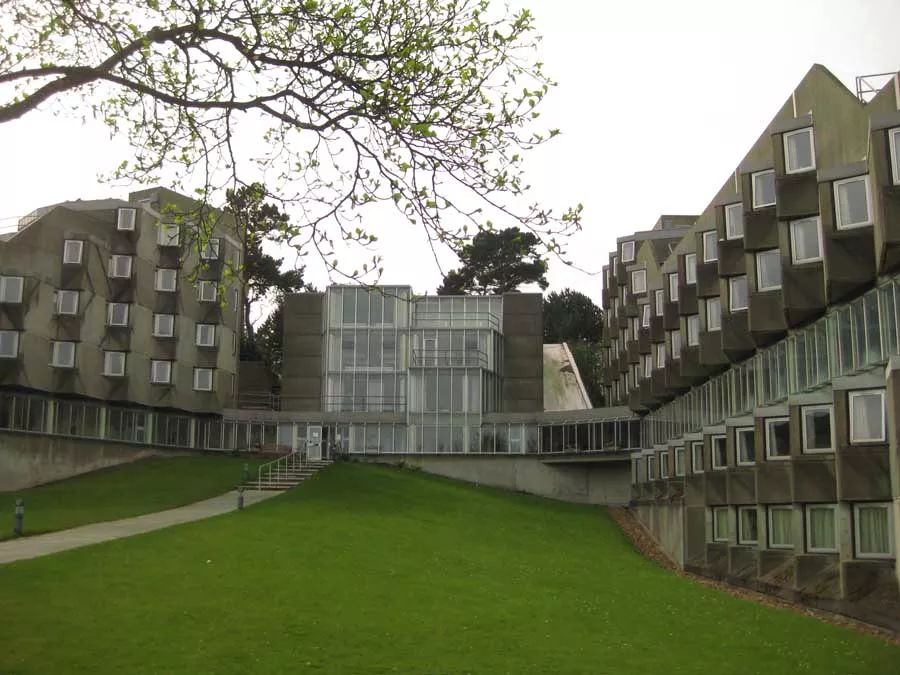
It was purposely designed as a historic courtyard, tower, corridor and a central object that you can identify to replace the traditional fountain or statue built during the founding of the college
.
Although it is difficult for people to find the common features of James sterling’s works because of this strong transformation, in fact, his unique design ideas are still reflected in his architectural works
.
Born in Glasgow, England in 1926, Stirling graduated from the Department of architecture of the University of Liverpool and started his business with his partner James Gowan in 1956
.
We put art in architecture and put the display of architectural structure in the second place
.
The lower part of the latter part of the classroom overhangs outwards, and the inclined wall also serves as the door head of the entrance and exit
.
Seven years later, they have designed some very distinctive projects at that time
.
The lower part of the tower consists of two stepped classrooms
.
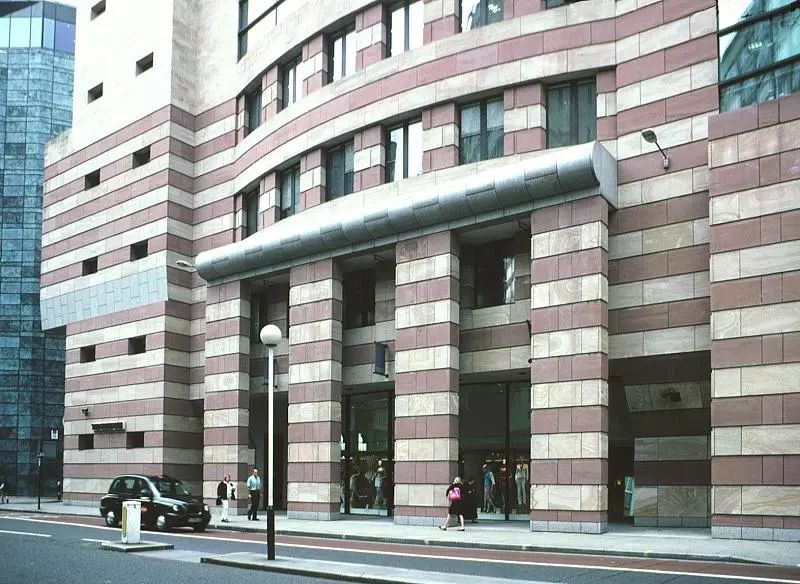
Since 1980, he has completed the expansion of a large social science center in Berlin, an art performance center at Cornell University and the Tate Gallery in London
.
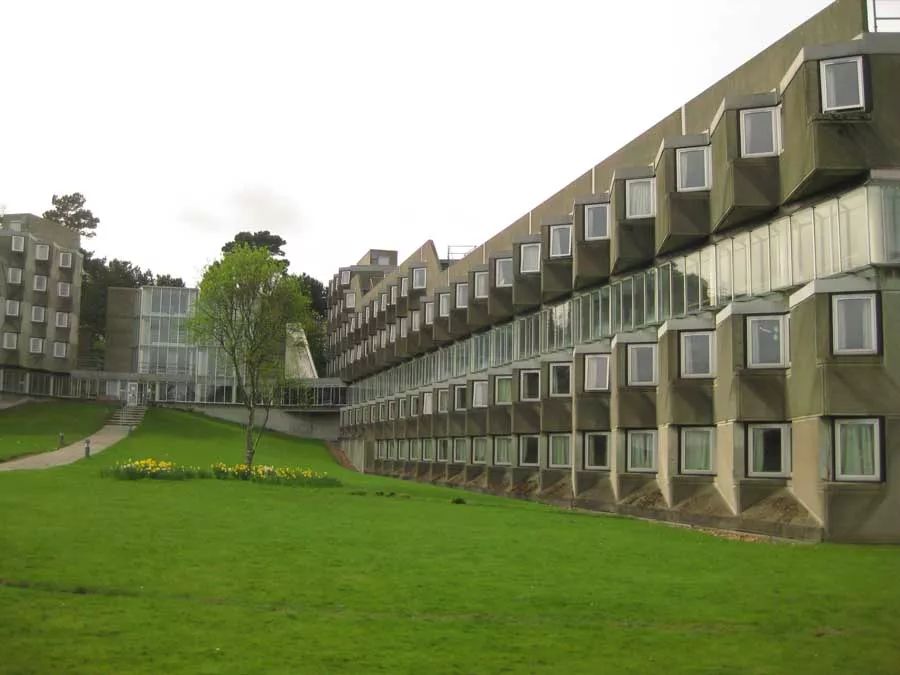
Many years ago, we built such a building in Oxford (the Florey building, Queen’s college, Oxford, 1971)
.
In 1941, James graduated from qualik senior high school in Liverpool; in 1942, he entered the school of art in Liverpool; from 1945 to 1950, he studied in the school of architecture of University of Liverpool and obtained a degree in architecture; from 1952 to 1956, James Sterling participated in ICA independent group and engaged in architectural design
.
As one of the most famous architects in Britain, James Stirling’s famous work was designed in 1963
.
Due to the relative limitation of space, the experimental workshop can not carry out the “big action” of external modeling, while the indoor space can be changed arbitrarily
.
Throughout many of James Stirling’s works, the style and technique of his architectural works are not directly related, but in response to the demands of the changing times
.
In his later years, James Stirling’s design thought seems to be exploring the essence of modern architecture all his life, but there is no extreme design thought and fanatical religious belief
.



