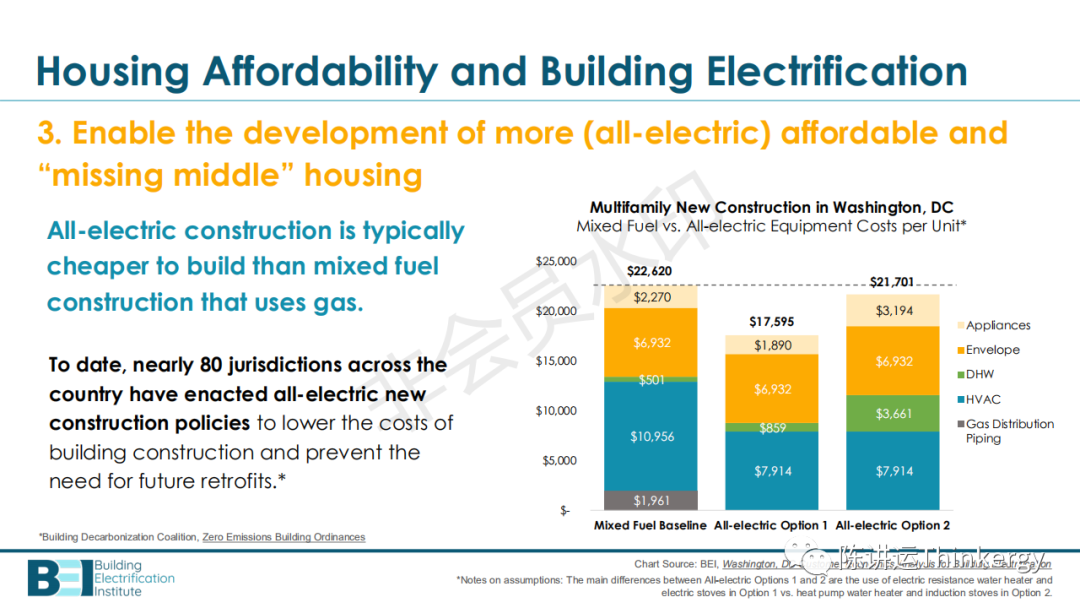
Spending 30% of the remaining income on very low household income is much less than spending 30% on high income.



Rent assistance housing: funds for obtaining rent payment assistance are usually distributed to tenants in the form of housing vouchers (also known as “Article 8 Housing” at the federal level).

Disadvantages: the percentage of household income is a blunt tool that underestimates the disproportionate impact on low-income people.
The “extreme housing cost burden” is usually defined as the rent and housing cost that families pay more than 50% of their income.

The “housing cost burden” is usually defined as a household paying more than 30% of its income in rent and housing costs.

Public housing: public and operated (usually operated by local governments) housing for residents eligible for income.


This may or may not include restrictions on the allowable resident income level, and / or may be related to specific tenants.

Subsidized affordable housing: housing that receives tax credits, grants and / or loans in exchange for rent restrictions and / or income level restrictions.



 Solid Lifting Socket Cross Pin
Solid Lifting Socket Cross Pin
Rent controlled housing: limit how much rent can be increased, regardless of the subsidy.

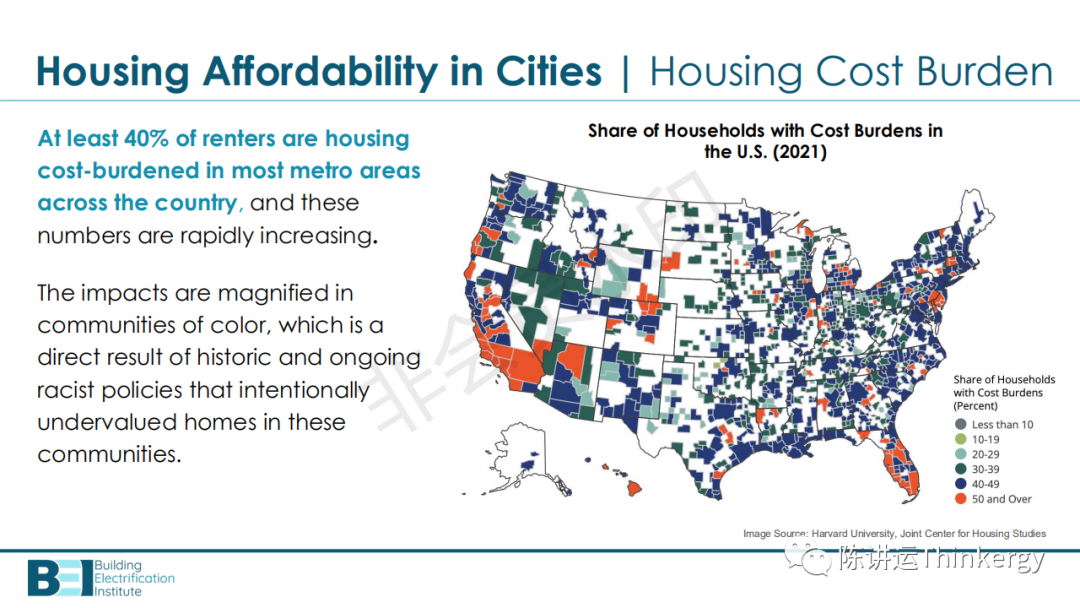
Affordable housing: a high-quality, healthy family whose total cost is in line with the family budget, and does not force residents to choose between other key needs (such as food, utilities, drugs and childcare services).





Compiled by: Chen dianyun.
A common way to define whether housing is “affordable” is if the total housing cost is less than a certain proportion of residents’ income.


Defining housing affordability according to “housing cost burden” has advantages and disadvantages: advantages: it is necessary to have a standard and measurable definition of housing affordability to track the trend and progress of improving housing affordability.