By the Eastern Han Dynasty, longitudinal arch became the mainstream, and brick vaults built on rectangular and square tombs had appeared.
Roof forms are diverse: hanging mountains and veranda are the most common, and Xieshan and dunding have also been used.
Dougong is widely used, and the structural function is obvious, but the form is not unified; ② Multi storey timber framed buildings have become more common, and the structure and construction technology of timber framed buildings have made great progress; ③ However, piyong and religious buildings in the Ming hall still use the form of high-rise buildings in the spring and Autumn period and the Warring States period, reflecting the technical problems of large space architecture that had not been solved at that time.


The pictures in the text are from the Internet.
The Han mountains and rivers are intact, and the ruins of the spring and Manchu dynasties still remain in CAI, and you people came out of the Han Dynasty.
There were two kinds of barrel vaults, longitudinal masonry and parallel masonry.
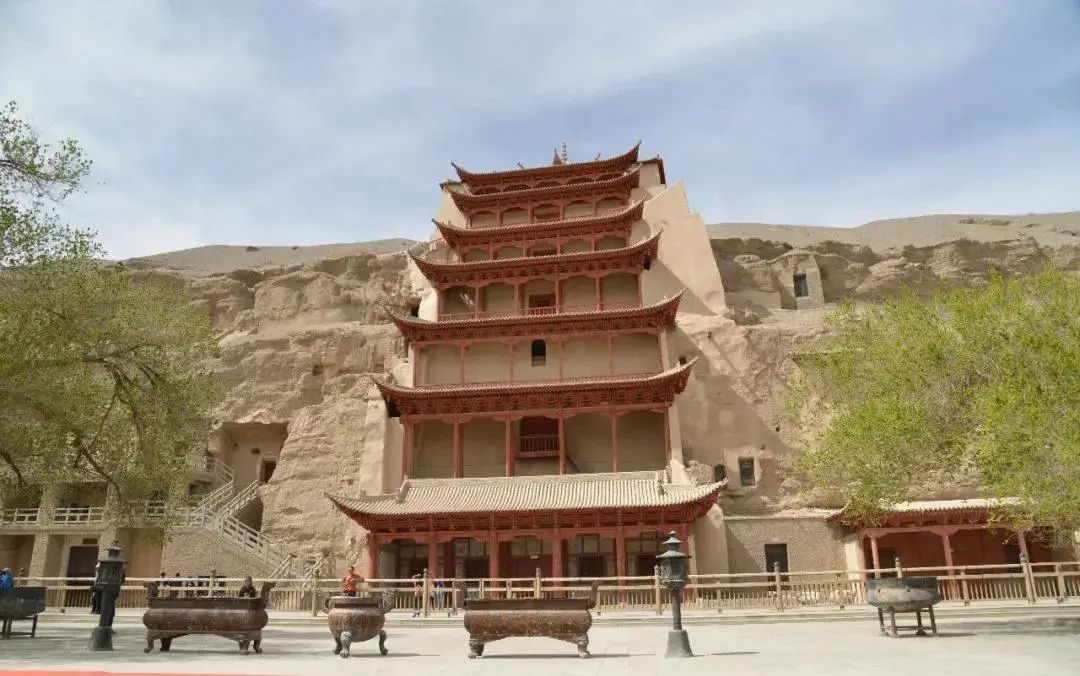
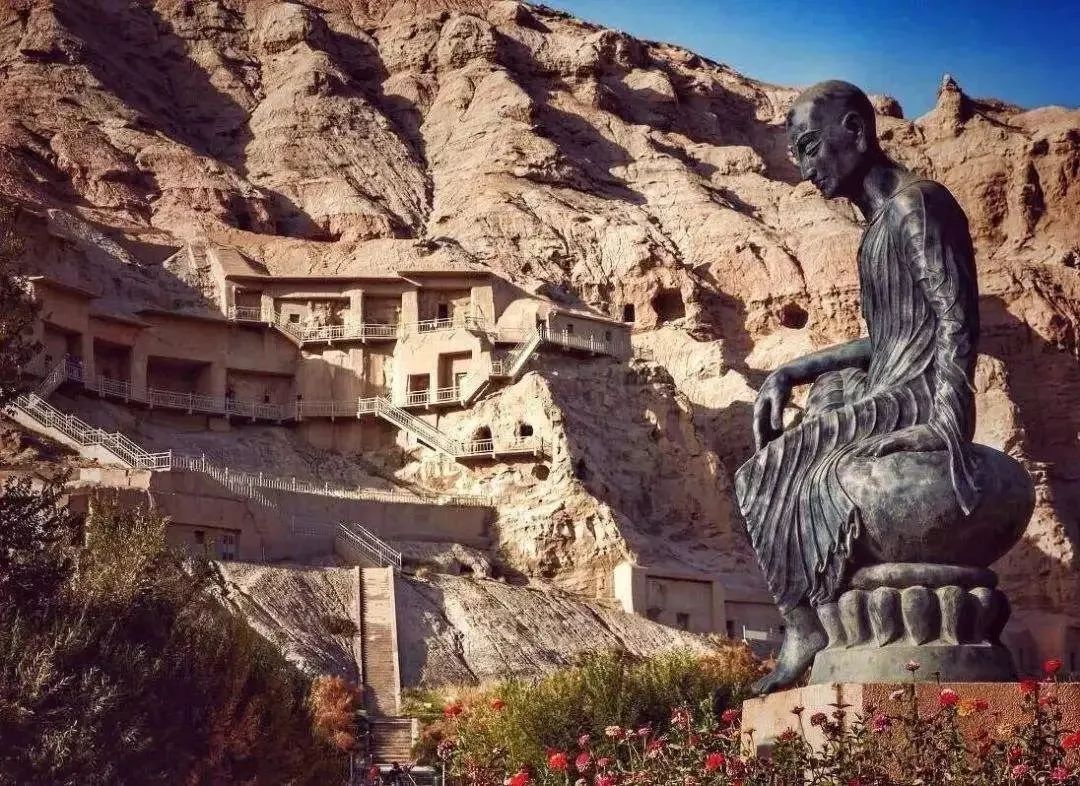
Qian Xingxiangzi · topic Luofu architectural style: from the simple architectural style of the Han Dynasty, it has become mature and round; Due to the introduction of Buddhism, Buddhist architecture began to develop, mainly including Buddhist temples, pagodas and grotto Temples: ① influenced by India, Buddhist temples took pagodas as the main worship object in the early stage, placed in the center of Buddhist temples, supplemented by Buddhist temples, placed behind pagodas; In the later stage, houses were converted into temples, the front hall was converted into a main hall, and the back hall into a lecture hall, which also made the original private gardens become part of Buddhist temples, which are often places for citizens to visit; The former is represented by the Yongning Temple in Luoyang in the Northern Wei Dynasty, with an intermediate tower, doors on all sides, and a Buddha Hall behind the tower; ② The emergence of high-rise pagodas, mainly wooden pagodas in the early stage, represents the most magnificent Yongning Temple Pagoda; Stone pagodas and brick pagodas appeared in the later period, representing the Songyue Temple Pagoda in Dengfeng, Henan Province, which is the earliest extant Pagoda in China.

The wind and smoke are all over the hole, and the moss is covered.
The rocks on the bank lean against each other, and the windows are pine and withered.
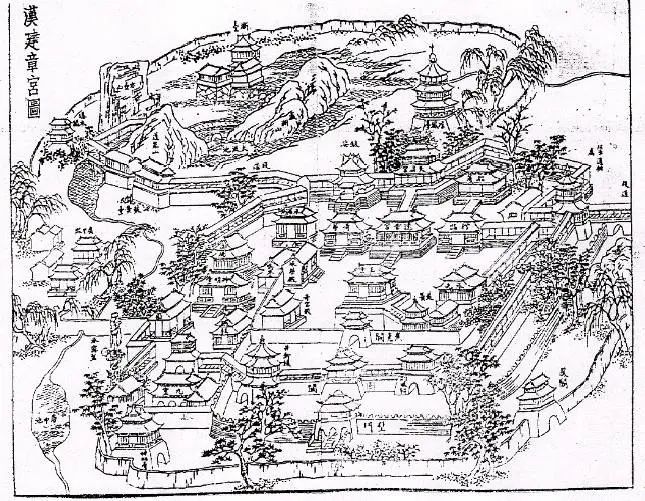
As soon as you go, you don’t need to use your skills—— To the most beautiful mountains and rivers, the most beautiful Heritage City: large scale, but lack of organic combination between buildings; It represents the multi palace system of Chang’an in Han Dynasty; Adopt the layout of Grand Palace, small palace, and forest, wood, pond and marsh; Architectural style: the rustic wood structure is becoming more and more mature: ① the beam lifting type and the bucket passing type (the combination form of the two wood components) have been formed.

③ Grotto temple is a cave shaped Buddhist temple dug on the cliff, which is divided into three types: tower type, Buddha Hall type, and monastery type, represented by Yungang Grottoes in Datong, Shanxi Province, Longmen Grottoes in Luoyang, Henan Province; The natural landscape garden has made great progress: on the one hand, the noble and powerful families pursue a luxurious life and take the garden as a place for sightseeing, feasting and entertainment; on the other hand, the scholar bureaucrats regard the landscape as elegant, which promotes the prosperity of the natural landscape garden; During this period, people’s material cognition of gardens began to turn to aesthetic cognition; Start to open ponds to divert water, pile soil into mountains, plant forests and gather stones, build Louguan houses, and imitate natural mountains and rivers.
Great progress has been made in masonry construction: ① great progress has been made in brick making technology, creating wedge-shaped and mortised bricks for building sewers and tombs; ② The arch structure was further developed.
Stone tombs include beam slab tombs, arch tombs, rock tombs, cliff tombs, etc., which represent the stone tombs in Yinan, Shandong, and others include tomb que, tomb shrine, tomb table, stone beast, stone tablet, etc., which represent the tomb stone que of Gaoyi, the governor of Yizhou in the Eastern Han Dynasty in Ya’an, Sichuan.
In addition, single-layer pagodas also appeared at that time.
This steep way was convenient for formwork free construction, and made the tombs relatively high and open; ③ A variety of architectural forms have been produced.
If there is infringement, please contact to delete -the.
The stone tower is high, and the apes cry and laugh at the peach blossom flowing down Qingchuan at night.
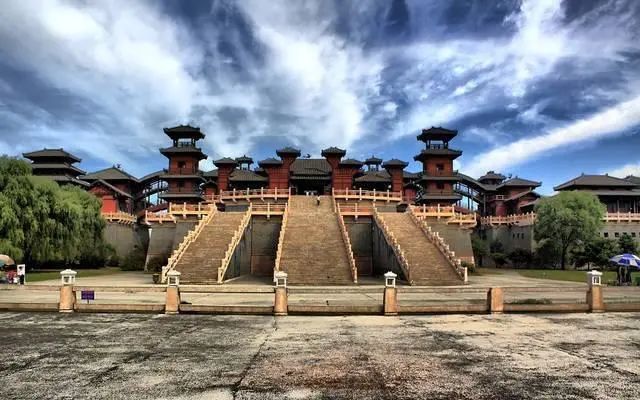

Natural landscape gardens rose from the Qin and Han Dynasties: mainly imperial hunting grounds, manors and palaces; On behalf of Emperor Wu of the Han Dynasty, he built Zhang palace, Three Kingdoms of the northern and Southern Dynasties, two Jin Dynasties, two watch clouds, three watch months, and four watch days.
The gate is deep and the path is barren, and the platform is far away from the peak.


