In fact, to some extent, this building is only an incomplete imitation of the temple buildings in China’s northern and Southern Dynasties
.
In fact, according to our opinion, this thing is a semi cave house
.
Sister Ono’s mission coincided with the transition period from China’s northern and Southern Dynasties to the Sui Dynasty
.
in fact, according to archaeology, this thing was built no earlier than the 7th century, but this architectural form certainly did not appear in the 7th century, It is generally believed that it is also a style that has existed since the ancient tomb era
.
First of all, the origin of architecture is a little similar, but the volume and production mode of the two civilizations are too different, which also led to the late Warring States period, Japan has just moved from the “rope man age” (じょうんじだいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいいい
.
However, in that era, the wealthier classes did not live in such things
.
Soon, when the dying age developed to a certain extent, the “Daiwa” (やまと) regime appeared in the immigrants
.
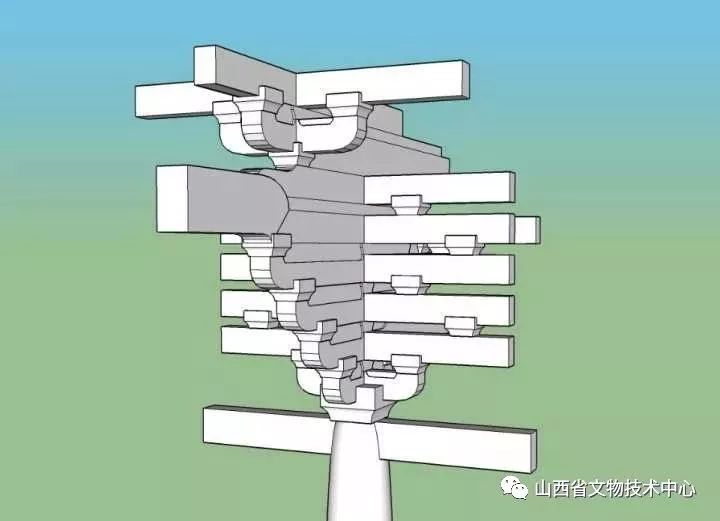
There are two “Qianmu” and “bonito wood” like fish bones
. 
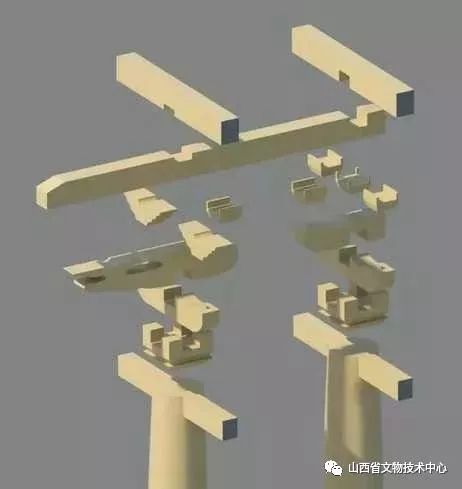
It can be seen that these buildings are basically made of a pile of wooden columns inserted on the ground, and then the house is built on it
.
Of course, if we say Buddhism, there must be a Buddhist temple
.
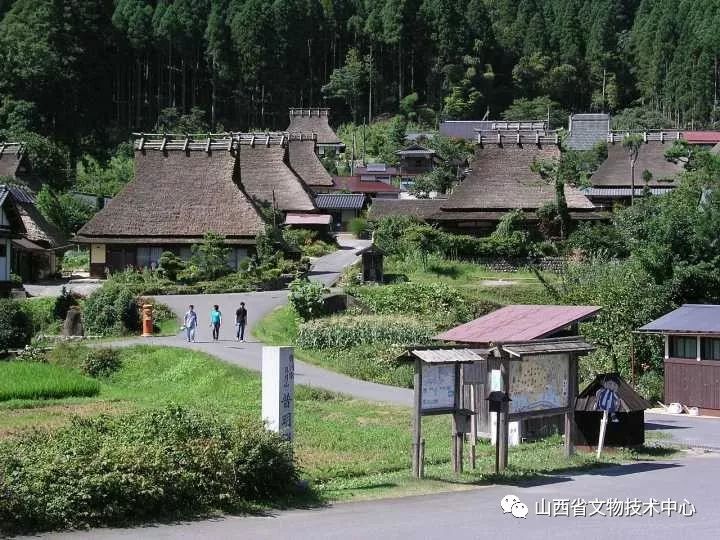
In the “thatched cottage village” near Kyoto, Japanese houses and even ceremonial buildings have been in this style for quite a long time, even until the Meiji Restoration, so we must remember this big head, which has a deep impact on Japanese architecture
.
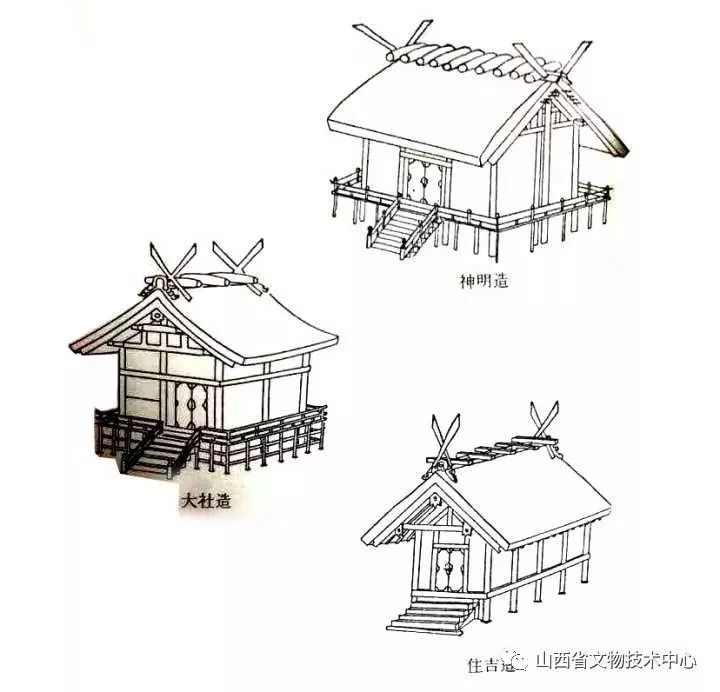
It can be seen from tuishe shrine that many elements of this building have been mentioned above, except for structural stability
.
In the era of Prince St
.
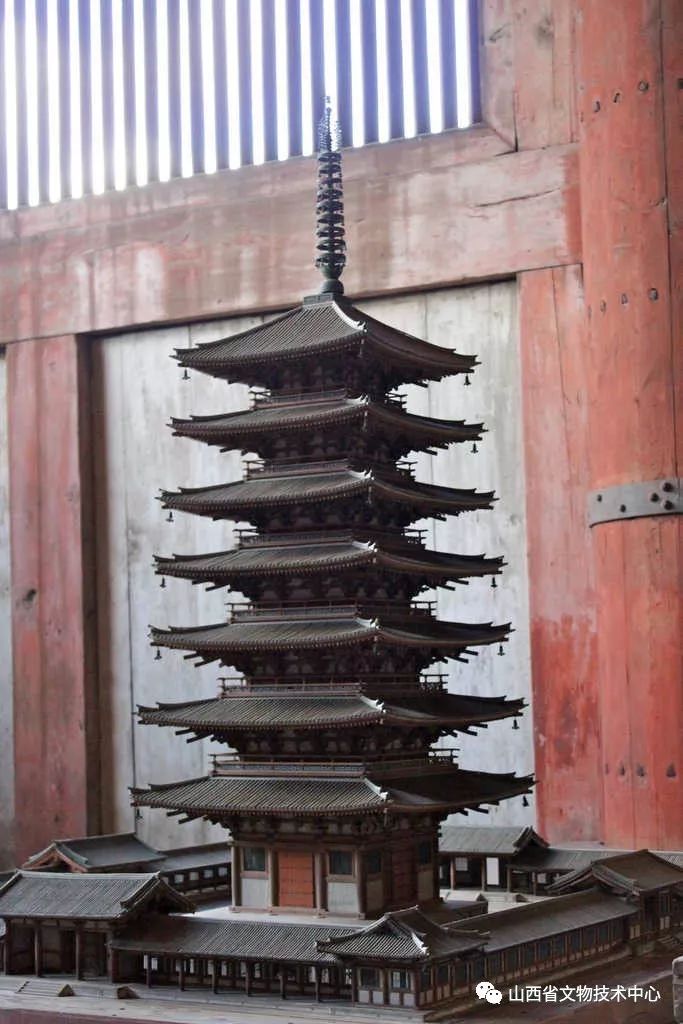
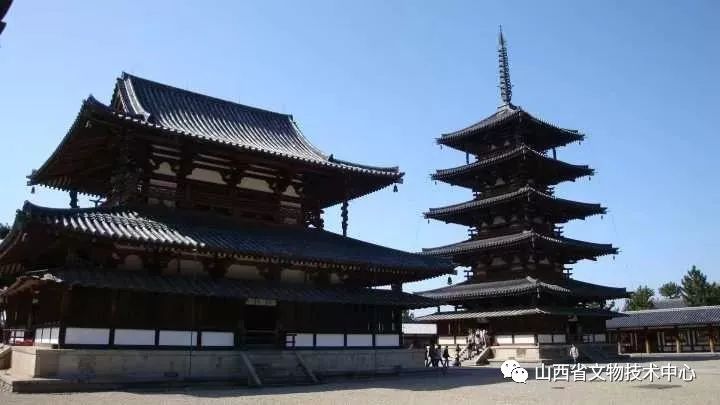
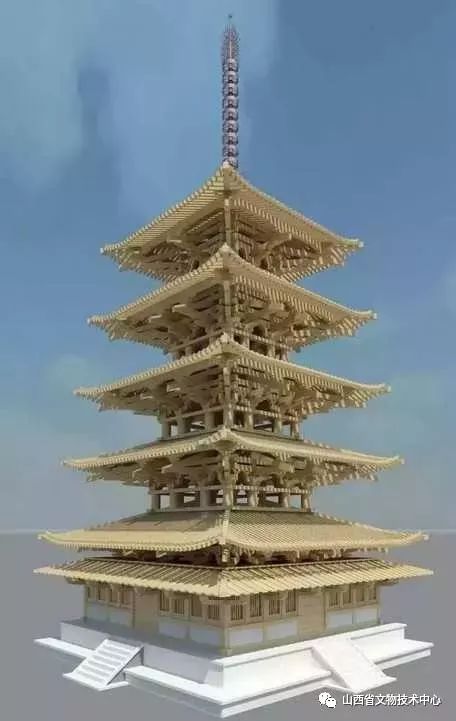
The seven heavy pagoda of tudong temple has some flavor of our early Buddhist temple
.
We should also know the “480 temples in the Southern Dynasty, many buildings in the misty rain” in the period of emperor Xiao Yan of Liang Wu.
. 
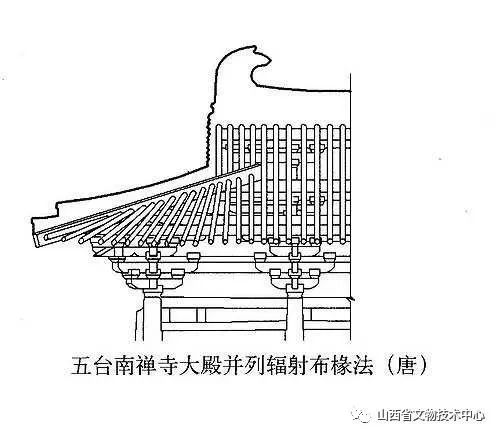
Let’s take a look at the FaLong temple
.
According to our words, it is “dry fence house”
.
The “Sui emissary” represented by sister Ono, as the hope of Prince Shengde to reform the Japanese country and fight against the Haozu, risked a narrow life to go to the Sui Dynasty in the hope of bringing the most advanced knowledge and technology to Japan
.
Therefore, since the day of the construction of the Yishi shrine, there has been a tradition – the annual relocation of the Palace (しきねんせぐう)
.
Therefore, the roof repair is very steep, and two horns “fly” out of the top part
.
Because the king of Daiwa regime always had to repair the huge square and round tombs, Japan entered the “ancient tomb age”
. 
They continued to conquer these Japanese aborigines
.
A fundamental reason for mentioning this kind of building is that the thatched roof used in this kind of building has always been an important feature of Japanese folk houses and even shrines
.
Moreover, Japanese architecture is very different from its own soil with the changes of the times
.
Nara FaLong temple FaLong temple is known as one of the earliest wooden buildings in Japan
.
They don’t want anything to be preserved forever, but let it continue in another way
.
He made Japan have systematic laws and regulations, and wrote “peace is the most precious” into the constitution
.
In fact, we see that many ancient buildings in Japan are so new, mostly because they are constantly renovated
.
This kind of roof repair is a process of forming a roof by splicing soft wood chips one by one
.
The concept is that this time has passed since Emperor Guangwu Liu Xiu established the Eastern Han Dynasty
.
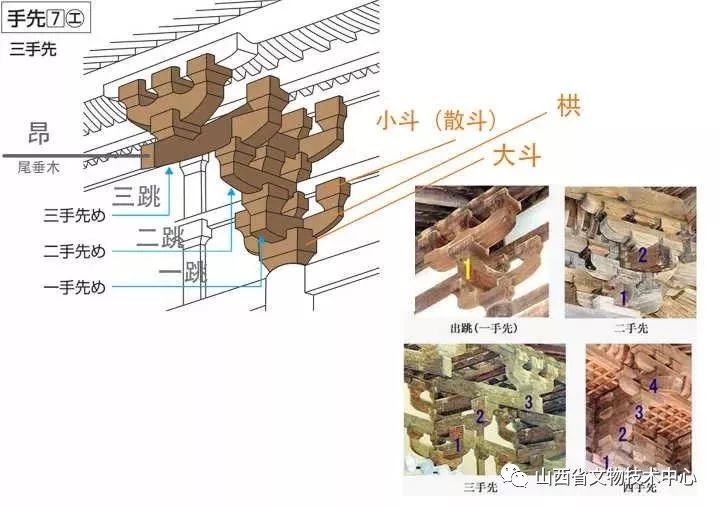
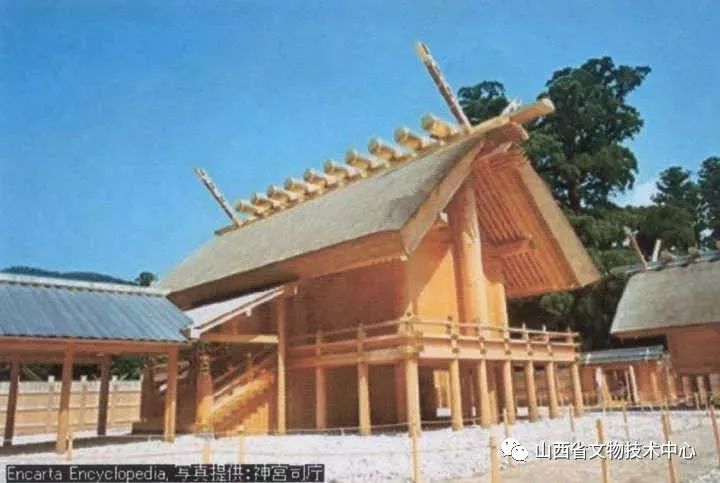
In this way, the unique Japanese shrine architecture that combines the dry column style and Mao repair described above has developed – the three earliest shrine styles in Japan( In the book.) So let’s take a look at the shrine “Yishi Shrine”, which was the earliest handed down in Japan and dedicated to the great God Tianzhao
. 
It was a kind of building with Buddhist pagodas built in the middle, corridors set in all directions and worshipped by believers in circles, for example
. 
I think it’s better not to compare the buildings of one era in China with all the buildings in Japan
.
By the way, the Japanese call the roof “root” (やね)
.
At first glance, it is very similar to Chinese architecture, almost completely getting rid of the original architectural model in Japan
.
In fact, this form has a deep impact on later Japanese buildings
.
Later, it was also widely used in higher specification building facades
.
At the same time, the prince is also a senior Buddhist
.
In fact, when Buddhist buildings were introduced to China from India through the western regions, many Temple models in China were not like this
.
In fact, if we understand history, we will find that whether it is Ashoka in India or Constantine in Rome, Religion is always the most suitable weapon for these leaders to deal with the fierce social contradictions of transformation
.
In fact, the Japanese call this “pillar digging building” (ほったてばセらたての), which is also an architectural model that continues from rope pattern to dying and even continues in Japan
.
This denglu site is something from the 1st century
.
Japan calls this thing “thatch” (やぶき), and this thatch can be said to be one of the four roof materials in Japan
. 
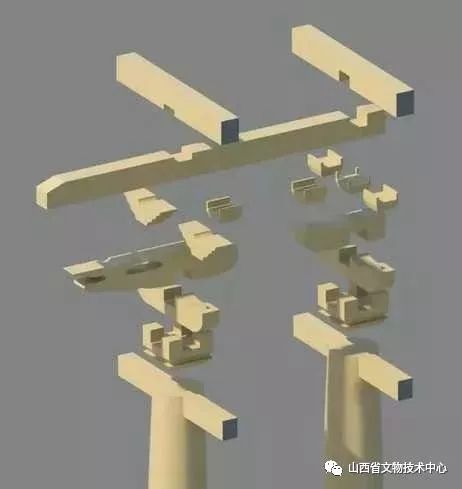

This is also one of the four roof technologies in Japan
.
There are many such things in Banpo site, but Banpo site has to be more than 6000 years away now
.
That is to say, every 20 years, a new shrine will be built in the nearby open space until the old shrine decays, Continue to build another one, and this shrine has been preserved in this way
.
Of course, this architectural model is not suitable in Japan, which has a maritime monsoon climate, wet and rainy in summer and snowy in winter
. 
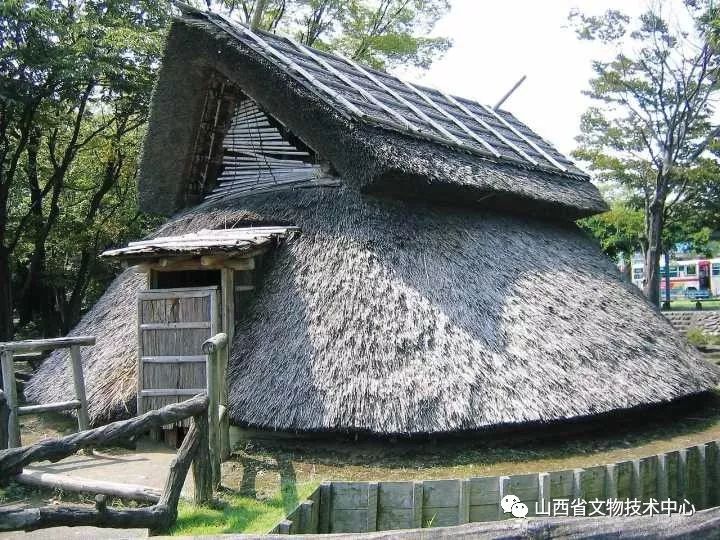
Figure “vertical cave dwelling” (たてあなしきじゅうょ) in the “denglu ruins (とろいせき)” in Japan
.
According to archaeology, although most civilians were half underground caves, another common housing structure in that era also affected Japanese architecture all the time
.
I often hear people who travel to Japan say to me, “you see, the buildings of the Tang Dynasty are basically preserved in Kyoto”, not to mention whether the buildings of the Tang Dynasty are really “higher” than those of the yuan, song, Ming and Qing Dynasties, I don’t know where it came from
.
The picture shows the ruins of sanneimaru mountain in Akita
.
Through archaeological investigation, although there are no buildings left in the ancient tomb era, it is certain that in the construction of the roof, an upgraded version of Mao repair, persimmon repair (こけらぶき), has appeared
.
In short, Japanese buildings at this time still smell like primitive tribes in Southeast Asia, The Japanese have a concept of “impermanence” since ancient times
.
This is the “divine creation” (しめいづり) written on it
.
It is inferred from Japanese history books that this was built in the 1st century A.D
. 
For example, the most famous white horse temple in Luoyang was not a temple with a central axis and the same as the Forbidden City
. 

De, the capital has been moved to the “flying bird” next to Nara
. 
Of course, not to mention that the Dongda temple was destroyed once later, it is not as early as the FaLong temple built during the reign of Prince Shengde
.
There are many such things at Hemudu site in Yuyao, Zhejiang Province, with a period similar to Banpo, This building model is very suitable for wet and rainy places, but in China, this building model was soon replaced by the high rammed earth platform in the Central Plains
.
Let’s have a look
.
Emperor Wu of the Han Dynasty has been dead for 100 years, and they still live here
.
But this is a treasure for Japan
.
Its waterproof and aesthetic properties are higher than the original thatch
.





